Coexist | Chapter 4.1
AI as a Mirror of Ourselves: Embracing Relationships | Human & Machine Relationships
Welcome to another installment of Coexist, a space dedicated to reflecting upon and interpreting the intersections between design, technology, humans, humanity, ethics, and justice.
If you haven't yet subscribed, I invite you to join us below.
Hello, dear readers,
We will continue the sequence of the macro chapter titled AI as a Reflection of Ourselves: Embracing Relationships. In the first edition of this subject, I delved into the concept of transdisciplinarity, an experimental approach that transcends traditional disciplinary boundaries to address complex challenges spanning multiple fields. It emphasizes the importance of acknowledging the complexity of problems, diverse perspectives, and the need to bridge the gap between abstract and specific knowledge. Two case studies illustrate the practical application of transdisciplinarity. The first case focuses on Neri Oxman, a designer known for her innovative approach that integrates biological principles, advanced fabrication techniques, and sustainability into her work.
The second case highlights the Willem de Kooning Academy (WdKA) in Rotterdam, which adopts an innovative and transdisciplinary approach to education. WdKA emphasizes transdisciplinary learning, critical thinking, and practice-based education, fostering dynamic laboratories where students from various fields collaborate to prototype and refine ideas, integrating emerging technologies to tackle contemporary challenges. For those who missed it, you can revisit Chapter 4.0 here.
Now, let's embark on Chapter 4.1.
AI as a Mirror of Ourselves: Embracing Relationships | On Humans & Machine Relationship
Join us in our upcoming Event on May 16th to discuss this and more.
AI acts as a reflection of humanity, unveiling the realities we encounter as individuals and as a society. These systems mirror the values, beliefs, and biases of their human creators and users, shaped by the data they ingest, the algorithms they employ, and the goals they pursue within their operating contexts. Thus, technology embodies a distinctly human influence, showcasing how our behavior, characteristics, and capabilities impact specific situations, systems, processes, and outcomes.
We find ourselves at a pivotal moment, where we are establishing novel connections with machines while witnessing the dawn of a new technological era.
With Coexist, we aim to discern the evolving relationships between humans and machines. There are diverse perspectives on how we ought to engage with AI and machines.
We strive to acknowledge the fact that AI is neither superior nor inferior; it possesses the potential to evolve into what we desire it to be.
Over the years, we've witnessed the evolution of AI, aiding processes, enabling personalization, and supporting us in various tasks.
We, at coexist are deeply intrigued by the diverse forms of relationships that have emerged since the onset of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. While automated cars and robots were impressive, recent years have unveiled more unexpected and fluid interactions with machines. we’ve observed how bots have transformed into virtual companions for humans, how robots are fostering meaningful connections with children and the elderly, and how the "metaverse," encompassing not only virtual but mixed reality, is facilitating new forms of interaction between the virtual and physical realms. Suddenly, an advanced text-based AI (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Gemini, etc, have entered our daily lives, exerting an unprecedented impact on our everyday routines, work, and more. Naturally, our fascination has grown, prompting us to explore its workings, its influence on our behaviors and expectations, and its revolutionary effects on various domains like language, work, education, and processes.
In this particular realm, we aim to delve deeply into the new dimension of creativity that generative AI, particularly ChatGPT from OpenAI, brings to the forefront. Understanding the underlying concepts surrounding this product is crucial for gaining insight into its workings and optimizing interactions.
Let's begin by defining some key subjects that revolve around the product ChatGPT:
What is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is a language model developed by OpenAI. It is part of the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) family of models, specifically based on the GPT-3.5 architecture. ChatGPT is designed to understand and generate human-like text, making it well-suited for conversational applications. It has been trained on diverse internet text and is capable of performing various natural language processing tasks, such as answering questions, generating creative content, providing language translation, and more.
The model operates by predicting the next word in a sequence of text, given the context of the preceding words. It has a large number of parameters, allowing it to capture complex patterns and generate coherent and contextually relevant responses in natural language. Users can interact with ChatGPT by providing prompts or queries, and it responds by generating text based on its training data.
What are GPTs?
GPTs are customized versions of ChatGPT that empower users to tailor the language model for specific tasks or contexts without requiring coding skills. Users can create, share, and explore these personalized versions, enhancing ChatGPT's utility in daily life, work, and various activities. Key features include privacy controls, the ability to define custom actions through API connections, and enterprise integration for internal use.
What is a Prompt?
A prompt, in the context of language models like ChatGPT, refers to the input provided to the model to generate a response. It is a specific instruction or query given to the model to elicit the desired output. The prompt serves as a guide for the model's language generation, influencing the type of response it produces. Users interact with the model by inputting prompts to receive relevant and context-specific answers or text. The effectiveness of the prompt plays a crucial role in shaping the output generated by the language model.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems, particularly machine learning models, that have the ability to generate new content, such as text, images, or other forms of data. These systems can create novel outputs based on the patterns and information they have learned during training.
What are Neural networks?
Definition: Neural Networks are computational models inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain's neural networks. They consist of interconnected nodes or artificial neurons organized in layers. Each connection has a weight, and the network learns by adjusting these weights based on input data.
Components:
Nodes/Neurons: Basic units that receive input, apply a function, and produce an output.
Layers: Neurons are organized into layers, including an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer.
Weights and Activation Functions: Weights on connections determine the strength of signals, and activation functions introduce non-linearity.
Types:
Feedforward Neural Networks (FNN): Information travels one way, from input to output.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN): Connections form cycles, allowing feedback loops.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN): Specialized for processing grid-like data, such as images.
What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are sophisticated natural language processing models that are trained on extensive datasets containing vast amounts of text data. These models belong to the category of artificial intelligence (AI) and are particularly designed for processing and generating human-like language.
Characteristics:
Scale: LLMs are characterized by their immense scale, often involving billions or even trillions of parameters.
Pre-training: They are typically pre-trained on a diverse range of internet text to learn grammar, context, and factual information.
Fine-tuning: After pre-training, LLMs can be fine-tuned on specific tasks or domains to make them more specialized.
So, we are talking about mechanisms but also language, and this is why it makes it so exciting, so familiar, so close to use.
I’ve been using ChatGPT already for a while, and the different interactions I’ve had I’ve been feeling it as an extension of my brain, mind, thoughts, ideas. It is bizarre but at the same time interesting what’s the feeling and companionships that it creates when you have to reach a goal with a specific output. It becomes a sort of partner, colleague, where you can put ideas and be complete through words, through language.
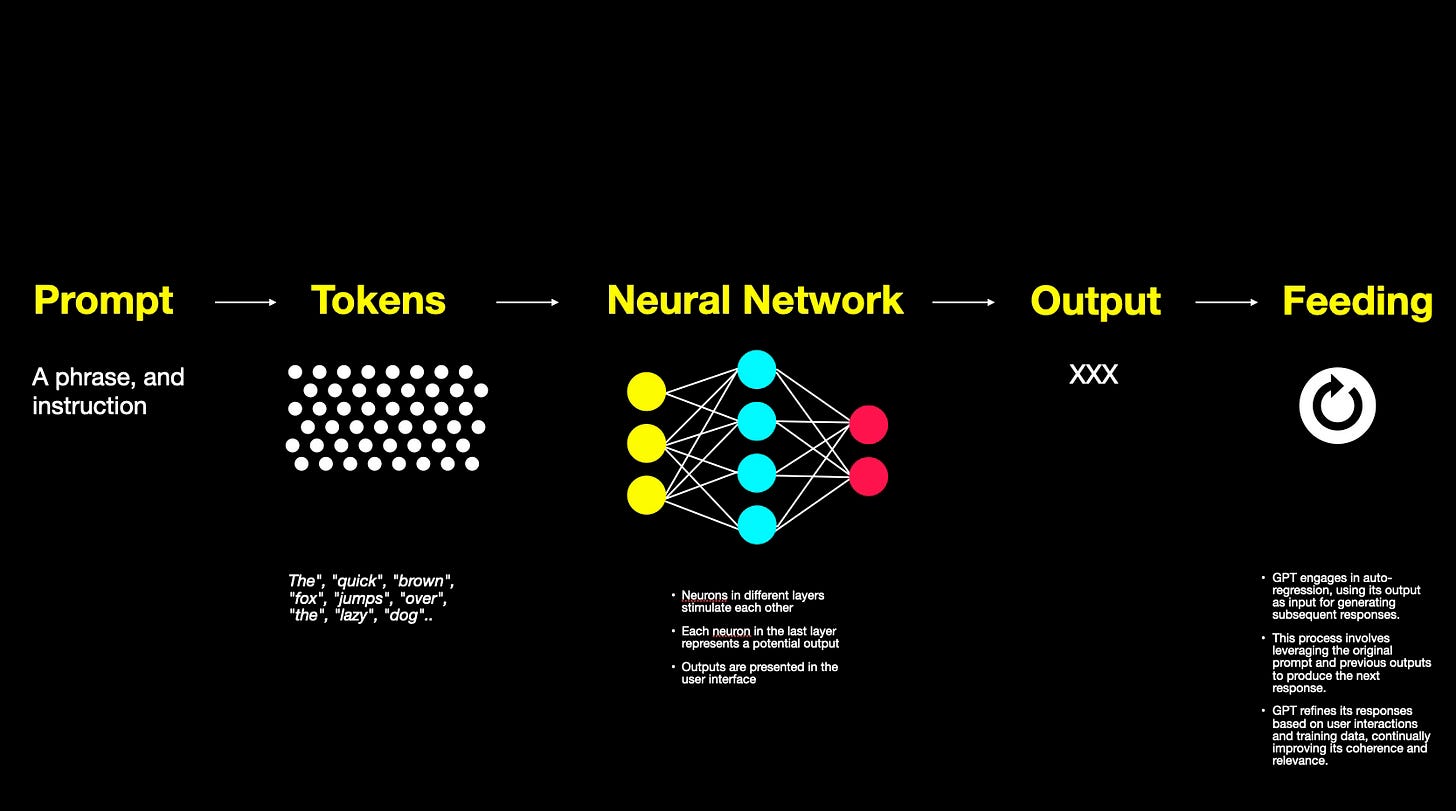
How the GPT works…
As previously discussed, GPT functions as a language model, distinct from a database, a reasoning engine, or a source of objective truth. While GPT excels as an interface layer atop a database or logic engine, it is not inherently one itself. It's crucial to understand that GPT does not operate as a standalone program running on a computer; rather, it functions as a neural network.
GPT lacks an inner monologue and cannot engage in thoughtful consideration. Any semblance of thinking or hesitation is illusory and may stem from server load or network latency. The thinking process of GPT is synonymous with the output it generates.
When text is inputted into GPT, it breaks down into tokens of words. Neurons in different layers stimulate each other, culminating in the last layer where each neuron represents a potential output, presented in the user interface.
Crucially, GPT utilizes this output and feeds it back into its own input, engaging in auto-regression. It leverages the original prompt and its own output to produce the next word or output. This process builds upon both your original question and everything GPT has learned so far, from both your interactions and its own training data.
Analyzing this process, I began to understand its potential usefulness, realising that it feels like: an active dialogue, resulting in an evolving output influenced by my input.
Virtual companions indeed perform a similar function, but here, the narrative begins to diverge as they become helpful and supportive in various mental processes. This interaction occurs in two ways: an internal loop—when you engage with yourself—or when you communicate with others (e.g., colleagues) to reach a consensus. The presence of language serves as an enabler, making the interaction somehow more human-like and distinct from previous interactions and relationships.
Essentially, with careful consideration, I can engage with a machine much like I do with a human—having a conversation and working together in a balanced and equal manner to achieve a goal.
Extended Thinking: A New Paradigm (?)
This chapter explores the concept of Extended Thinking, building upon the extended mind theory proposed by thinkers such as Andy Clark and David Chalmers. Traditionally, cognitive processes, including creative and analytical thinking, have been viewed as confined within an individual's mind, clearly separated from external influences. However, the extended mind theory challenges this perspective by suggesting that the mind does not end at the physical boundaries of the body but encompasses tools, environments, and interactions
This broader perspective implies that all forms of thinking—be it creative, logical, or problem-solving—are augmented by the external world. By integrating elements from our environment into our cognitive processes, thinking becomes not just an internal phenomenon but an interactively extended one. This chapter delves into how our understanding of thinking is expanded when we incorporate contributions from traditional cognitive tools and advanced technologies like large language models (LLMs). This approach offers a deeper insight into how humans interact with informational tools to enhance and extend their cognitive capabilities across various domains.
Traditional cognitive tools, such as notebooks, calculators, and software applications, have long served to extend human cognitive capacities. These tools facilitate the external storage, retrieval, and manipulation of information, thereby reducing cognitive load, aiding memory, and offering structured approaches to problem-solving.
Large Language Models (LLMs), like ChatGPT, might represent a further evolution in the augmentation of human cognition. Unlike traditional tools that mainly store and retrieve information, LLMs access vast databases of knowledge and generate new content from learned data patterns. They are capable of synthesizing and inferring information and, in some instances, predicting outcomes based on user queries. This capability transforms LLMs into dynamic cognitive extensions, enabling deep interactions in a conversational style and assisting with a diverse array of tasks including writing, coding, problem-solving, and acquiring new knowledge.
This comparison not only illuminates the potential of each approach but also their respective limitations. While traditional tools typically enhance specific cognitive functions, such as memory or calculation, LLMs provide a more holistic enhancement, capable of adapting to a broad spectrum of tasks. However, the effectiveness of LLMs is contingent upon the quality and scope of their training data, and they may not fully grasp the complexities or contextual nuances that a human mind can. Thus, while they extend our thinking capabilities significantly, LLMs also underline the importance of human oversight in tackling intricate or highly contextualized tasks.
Language as The Key Factor
Language serves as the primary medium through which Large Language Models (LLMs) operate, marking it as a critical component in their capacity to extend human cognition. Echoing Andy Clark's view, tools that aid cognitive processes are integral to our extended mind, particularly when they enhance our capabilities (Clark, 2003). LLMs exemplify this by providing linguistic scaffolding—supporting and enriching thought processes and idea development through conversational interactions. This scaffolding is not merely supportive but plays an active role in shaping the direction and quality of intellectual output.
In the realm of extended thinking, language transcends its conventional role. It does not simply facilitate communication; it becomes a transformative tool that bridges human cognitive limitations and digital potential. Through language, LLMs engage with users, parsing complex queries and offering responses that can illuminate new perspectives and synthesize diverse information sources. This interaction allows for a co-creative process that significantly surpasses traditional human-tool interactions.
The dynamic interplay between human linguistic input and machine language processing underlines the sophisticated level at which modern cognitive tools operate. By iterating on human ideas and providing instant feedback, LLMs foster a deeper exploration of concepts and enable a more nuanced understanding. Thus, language is not only a tool for communication but a pivotal factor in extending the boundaries of human thinking itself.
Human-like Interaction
The interaction facilitated by language between users and Large Language Models (LLMs) often mirrors human-like dialogue. Due to their ability to access and process vast amounts of data, and utilize language as a flexible medium, LLMs can engage in interactions that feel natural and less mechanistic. This human-like interaction is pivotal; it bridges various forms of cognitive assistance, making LLMs resemble colleagues, coaches, or mentors. Such capabilities expand the potential uses of LLMs across diverse fields and situations, enhancing their role as companions and supporters in cognitive tasks.
LLMs leverage linguistic interaction to provide tailored advice, generate creative ideas, solve complex problems, and support learning—functions traditionally associated with human partners in collaborative and educational environments. This transformative interaction suggests that relationships with LLMs could increasingly resemble those with human colleagues, providing a form of companionship that is informed by, and responsive to, the user's needs and input.
A significant limitation of LLMs, however, is their propensity for "hallucinations" or the generation of factually incorrect or misleading information. This issue stems from their reliance on patterns in data rather than a deep, contextual understanding of content. Despite their sophistication, LLMs do not possess true consciousness or critical reasoning abilities and can sometimes produce errors that might be contextually inappropriate or factually wrong.
This underscores the irreplaceable role of human interaction and oversight. While LLMs can significantly extend our cognitive capabilities, they do not replace the nuanced and critical engagement found in human discussions. Humans contribute a layer of objectivity and ethical judgment that is vital for evaluating the appropriateness and accuracy of machine-generated content. As such, even as we collaborate with these advanced tools, it remains crucial to maintain a dialogue not just with the LLMs but also among ourselves to verify and contextualize their outputs.
In conclusion, while LLMs, like Chatgpt enhance and extend our cognitive processes through sophisticated, human-like interactions, they do not supplant the need for human engagement. Instead, they should be seen as partners that contribute to a broader cognitive process, where human oversight remains essential to ensure the integrity and appropriateness of the outcomes. This partnership, blending human insights with machine efficiency, defines the new frontier of extended thinking—where technology enhances human capabilities without replacing the critical elements of human judgment and ethical considerations.
This reflection was written with contributions from Ciro Eleazar, involving many exchanges, iterations, and research through various LMMs, as well as some readings listed below:
Clark A., Chalmers D. (1998). The Extended Mind.
Sunshine L. (2017). Bakhtin, Theory of Mind, and Pedagogy: Cognitive Construction of Social Class.
Mattin D. (2023). Talking to Ourselves.
Thank you for reading and see you the next chapter.
Marihum
P.S. If you're interested in joining the discussion, sign up for the Coexist newsletter. Feel free to reach out if you'd like to engage in debates about these topics.